Science
Researchers Unveil Ferroelectric Fluids for Revolutionary Actuators
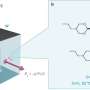
Researchers at the Institute of Science Tokyo have made a significant breakthrough by demonstrating that ferroelectric fluids can harness an overlooked property known as transverse electrostatic force (TEF). This discovery enables the fluids to rise over 80 mm without the need for magnets or high voltages, potentially transforming the field of electrostatic actuators.
By leveraging the spontaneous polarization and exceptionally high dielectric constant of these fluids, the team achieved a strong TEF that was previously thought to be unattainable in traditional electrostatic systems. Their findings, published in Communications Engineering, pave the way for the development of lightweight, energy-efficient motors that could operate at low voltages.
Understanding Electrostatic Actuators
Electrostatic actuators are devices that convert electrical energy into motion, playing a crucial role in modern technologies from microelectromechanical systems to robotics. Typically, these actuators rely on applying an electric field between two electrodes, which generates an attractive force known as Maxwell stress. However, this method requires high voltages to produce significant motion, limiting their applications.
For years, the TEF, which acts perpendicularly to the electric field, was considered too weak for practical use. As a result, electrostatic actuators were confined mostly to small, high-voltage applications, while larger systems often utilized electromagnetic or piezoelectric mechanisms.
The Role of Ferroelectric Nematic Liquid Crystals
The landscape began to shift with the advent of polar nematic liquid crystals. These ferroelectric nematic liquid crystals combine the flow properties of liquids with spontaneous polarization, allowing their molecules to collectively align and maintain an internal electric dipole. Notably, their dielectric constants can surpass those of conventional materials by several thousand times, facilitating substantial mechanical stress generation under modest voltages.
A research team led by Suzushi Nishimura and Tatsuhiro Tsukamoto set out to explore whether ferroelectric nematic liquid crystals could effectively utilize and amplify the TEF. Their experiments involved a mixture of DIO and DIO-CN, a eutectic liquid crystal blend stable between 22 °C and 52 °C. The researchers placed two parallel stainless-steel rulers inside a reservoir filled with the ferroelectric fluid, applying a direct current electric voltage while controlling the temperature precisely.
The results were remarkable. As the electric field increased, the liquid began to rise, showcasing a dramatic response. At just 28 V/mm, the fluid column lifted by over 80 mm, demonstrating the robust capabilities of the TEF. This motion corresponded to a stress exceeding 1,000 N/m², achieved at voltages significantly lower than those required by conventional electrostatic actuators.
Control fluids such as silicone oil did not exhibit similar movement, confirming the unique nature of the DIO/DIO-CN mixture. Electrical measurements indicated a smooth transition from the paraelectric to the ferroelectric state, validating that the amplified force stemmed from spontaneous polarization rather than standard dielectric behavior.
Through repeated trials, the researchers established the stability and reproducibility of the force, proving its potential for continuous operation. According to Nishimura, “By using a ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal whose dielectric constant and polarization are over a thousand times greater than those of conventional materials, we drastically reduced the required driving voltage, from around 10 kV to just a few tens of volts.”
This innovative design allows for the construction of a rotor entirely from plastic, streamlining the motor’s structure and enabling a lightweight, rare-earth metal-free, and sustainable build. The implications of this research are profound, indicating a major advancement in actuator technology.
Nishimura further emphasizes the significance of this work, stating, “As the global transition toward decarbonization accelerates and electric energy becomes a dominant power source, ferroelectric motors, free from rare-earth elements and operable at low voltages, are expected to contribute to a sustainable and resilient society.”
This pioneering study not only enhances the engineering of electrostatic devices but also redefines their potential applications in future technologies, marking a significant step toward more efficient and environmentally friendly solutions in energy conversion.
Science
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Reports Promising Results in Obesity Drug Trials

Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals announced promising early results from its gene-silencing drug candidates, indicating potential advancements in obesity treatments. The company revealed findings from an ongoing Phase 1/2 study that involved patients taking a drug named ARO-INHBE in combination with Eli Lilly’s Zepbound.
In the study, participants receiving the combination therapy lost an average of 9.4% of their body weight over a period of 16 weeks. In contrast, those treated with Zepbound alone experienced a weight loss of 4.8%. These results are particularly significant as they were observed in a cohort of patients struggling with both obesity and diabetes, a group that typically sees less weight loss from treatments compared to non-diabetic individuals.
Significant Fat Loss Observed
The data also highlighted substantial reductions in visceral fat, which is known to pose serious health risks due to its accumulation around vital organs. Participants receiving the combination therapy lost 23% of their visceral fat, along with 15% of their total fat and an impressive 77% of their liver fat. In comparison, those on Zepbound alone lost 7% of their visceral fat, 5% of their total fat, and 20% of their liver fat.
The ongoing trial suggests that Arrowhead’s approach may enhance the efficacy of existing treatments, potentially changing the landscape of obesity management. With these early findings, the competition among biotechnology firms to develop long-lasting weight loss therapies is likely to intensify.
Broader Implications for Obesity Treatment
As obesity rates continue to rise globally, the need for effective weight loss solutions has never been more urgent. The results from Arrowhead’s study could pave the way for new treatment options that offer greater efficacy for individuals with complex health profiles, such as those living with diabetes.
The pharmaceutical sector remains vigilant as these developments unfold. Investors and healthcare professionals alike will be closely monitoring the next phases of Arrowhead’s trials to assess the long-term viability and safety of ARO-INHBE in the treatment of obesity.
As more data becomes available, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how its gene-silencing technology can contribute to effective obesity management strategies, potentially improving the quality of life for millions facing this challenging health issue.
Science
Rethinking Infrastructure Design to Mitigate Disaster Risks

Disasters often provoke discussions centered on natural events, framing storms as “unprecedented” and floods as “once-in-a-century.” Yet, these descriptions overlook a crucial element: disasters occur within human-designed environments, which significantly influence their impact. The responsibility for these environments lies not only with nature but also with the systems that have been built, maintained, and sometimes neglected over time.
Infrastructure systems play a pivotal role in shaping how communities withstand and respond to disasters. According to a report from the United Nations, approximately 90% of urban areas are at risk from natural hazards exacerbated by climate change. This vulnerability stems from inadequate infrastructure planning and investment, which can leave populations exposed and unprepared.
Human Impact on Disaster Outcomes
The design and upkeep of infrastructure can either mitigate or amplify the effects of disasters. For instance, poorly maintained drainage systems can lead to severe flooding during heavy rain, while robust urban planning can enhance community resilience. The World Bank estimates that investing in resilient infrastructure could save up to $4.2 trillion annually in disaster recovery costs by 2030.
In many regions, the consequences of neglecting infrastructure are stark. Cities that fail to invest in their roads, bridges, and flood control systems face heightened risks during extreme weather events. In March 2024, a severe storm caused widespread flooding in a coastal city, resulting in damages exceeding $1 billion. The aftermath highlighted how outdated infrastructure contributed to the disaster’s severity, prompting calls for urgent reform in urban planning practices.
Recent events demonstrate that disasters do not merely occur; they are often the culmination of inadequate foresight and planning. For instance, when examining the climate change crisis, it becomes clear that communities with outdated infrastructure systems suffer disproportionately. These systems contribute not only to immediate physical risks but also to long-term economic and social challenges.
Building for the Future
The global community must reassess how infrastructure is designed and maintained. Sustainable urban planning can reduce disaster risks, ensuring that communities are better equipped to handle the effects of climate change. Innovative designs, such as green infrastructure and resilient building materials, can play a crucial role in this transformation.
Investment in infrastructure must prioritize resilience, integrating advanced technologies and sustainable practices. For instance, cities can implement smart systems that monitor environmental conditions and adapt in real-time, thereby enhancing response capabilities during disasters. Shifting the focus from merely repairing damage to creating adaptable infrastructure is essential for reducing future risks.
As the frequency and intensity of natural disasters increase, the need for a proactive approach to infrastructure design becomes critical. Governments and organizations must collaborate to develop comprehensive plans that consider the long-term impacts of climate change on urban areas. By prioritizing resilience, the global community can protect vulnerable populations and minimize the devastating consequences of future disasters.
In summary, while the language surrounding natural disasters often emphasizes their suddenness, it is essential to recognize the underlying human factors that contribute to their severity. By investing in robust infrastructure and sustainable planning, societies can significantly reduce their vulnerability to the impacts of climate change and create safer environments for future generations.
Science
Solar Storm Breaks Records: Active Region Observed for 94 Days

In May 2024, an unprecedented solar storm, the most powerful in two decades, occurred, capturing the attention of the scientific community. An international team led by researchers from ETH Zurich meticulously observed this event. Their findings are now crucial for enhancing space weather forecasts, which play a significant role in satellite operations and communications on Earth.
Record-Breaking Observations
The solar storm lasted for an exceptional period of 94 days, marking a notable extension of activity in a solar region. This duration surpasses previous records, offering new insights into solar behavior that can influence space weather. The team at ETH Zurich utilized advanced observational techniques to monitor solar activities, providing data that can improve predictive models.
Solar storms are known for their potential to disrupt technologies that rely on satellite communication. Such disruptions can lead to significant economic impacts, affecting industries that depend on precise satellite data. The prolonged nature of this recent storm indicates a shift in solar activity patterns, prompting scientists to reassess existing models.
Implications for Space Weather Forecasting
The findings from the ETH Zurich team not only highlight the storm’s intensity but also its implications for future forecasting. By understanding the characteristics and duration of solar storms, researchers can develop more accurate predictions of space weather events. Accurate forecasting is vital for protecting infrastructure on Earth, including power grids and communication systems.
In addition to improving predictive capabilities, this research underscores the need for continued investment in space weather research. The international collaboration involved in this study reflects a growing recognition of the importance of global efforts to monitor and respond to solar activities.
The implications of the May 2024 solar storm extend beyond scientific curiosity. For industries reliant on satellite technology, enhanced forecasting can mitigate risks and improve operational resilience. As scientists continue to analyze the data, the hope is that these insights will lead to a safer and more reliable technological landscape in the face of solar events.
As the research progresses, the scientific community anticipates more discoveries related to solar activity and its effects on Earth. The record-setting observation period established by the ETH Zurich team is a significant step forward in our understanding of solar storms and their potential impact on modern society.
Science
Researchers Identify Key Genes for Brain Development Using CRISPR
A groundbreaking study has identified hundreds of genes essential for the transformation of embryonic stem cells into brain cells. Led by Prof. Sagiv Shifman from The Institute of Life Sciences at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, in collaboration with Prof. Binnaz Yalcin from INSERM in France, the research employed genome-wide CRISPR knockout screens to investigate the genetic underpinnings of early brain development. The findings were published in the esteemed journal Nature Neuroscience on March 15, 2023.
The research team focused on understanding which genes play critical roles in the differentiation process of embryonic stem cells into neurons, a fundamental aspect of brain development. By utilizing CRISPR technology, they systematically knocked out genes across the genome to observe their effects on cell differentiation. This innovative approach allowed the researchers to pinpoint specific genes that, when disrupted, hindered the proper development of brain cells.
The implications of this study extend beyond basic science. Understanding the genetic requirements for brain development can provide insights into various neurological disorders. When the processes governing the formation of brain cells go awry, it can lead to conditions such as autism, schizophrenia, and other developmental disorders.
In their experiments, the team identified over 300 genes that are vital for the differentiation of embryonic stem cells into neurons. Among these genes, several were previously linked to neurodevelopmental disorders, suggesting that their disruption during early brain development could have significant consequences.
The researchers emphasized the importance of this work in contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of how genetic factors influence brain formation. As Prof. Shifman noted, “This study not only maps the genetic landscape of brain development but also opens new avenues for investigating potential therapeutic targets for neurodevelopmental diseases.”
The findings from this research may advance the field of regenerative medicine, particularly in developing stem cell therapies aimed at repairing brain damage or treating disorders rooted in early developmental abnormalities. Such advancements could pave the way for innovative treatment strategies that harness the power of stem cells to restore neurological function.
In conclusion, the research conducted by Prof. Shifman and Prof. Yalcin marks a significant step forward in the field of neuroscience. By uncovering the genetic requirements for brain cell development through cutting-edge CRISPR technology, this study offers valuable insights that could transform our understanding of the brain and its disorders. The ongoing exploration of these genetic factors will be crucial for future research and potential clinical applications in neuroscience.
-

 Top Stories4 days ago
Top Stories4 days agoPiper Rockelle Shatters Record with $2.3M First Day on OnlyFans
-

 Top Stories3 days ago
Top Stories3 days agoUrgent Update: Denver Fire Forces Mass Evacuations, 100+ Firefighters Battling Blaze
-

 Top Stories1 day ago
Top Stories1 day agoOregon Pilot and Three Niece Die in Arizona Helicopter Crash
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoTragedy in Crans-Montana: Fire Claims Lives of Holiday Revelers
-

 Entertainment5 days ago
Entertainment5 days agoIce-T and Coco Celebrate 25 Years Together in Love and Laughter
-

 Top Stories12 hours ago
Top Stories12 hours agoMeta’s 2026 AI Policy Sparks Outrage Over Privacy Concerns
-

 Top Stories4 days ago
Top Stories4 days agoOnlyFans Creator Lily Phillips Reconnects with Faith in Rebaptism
-
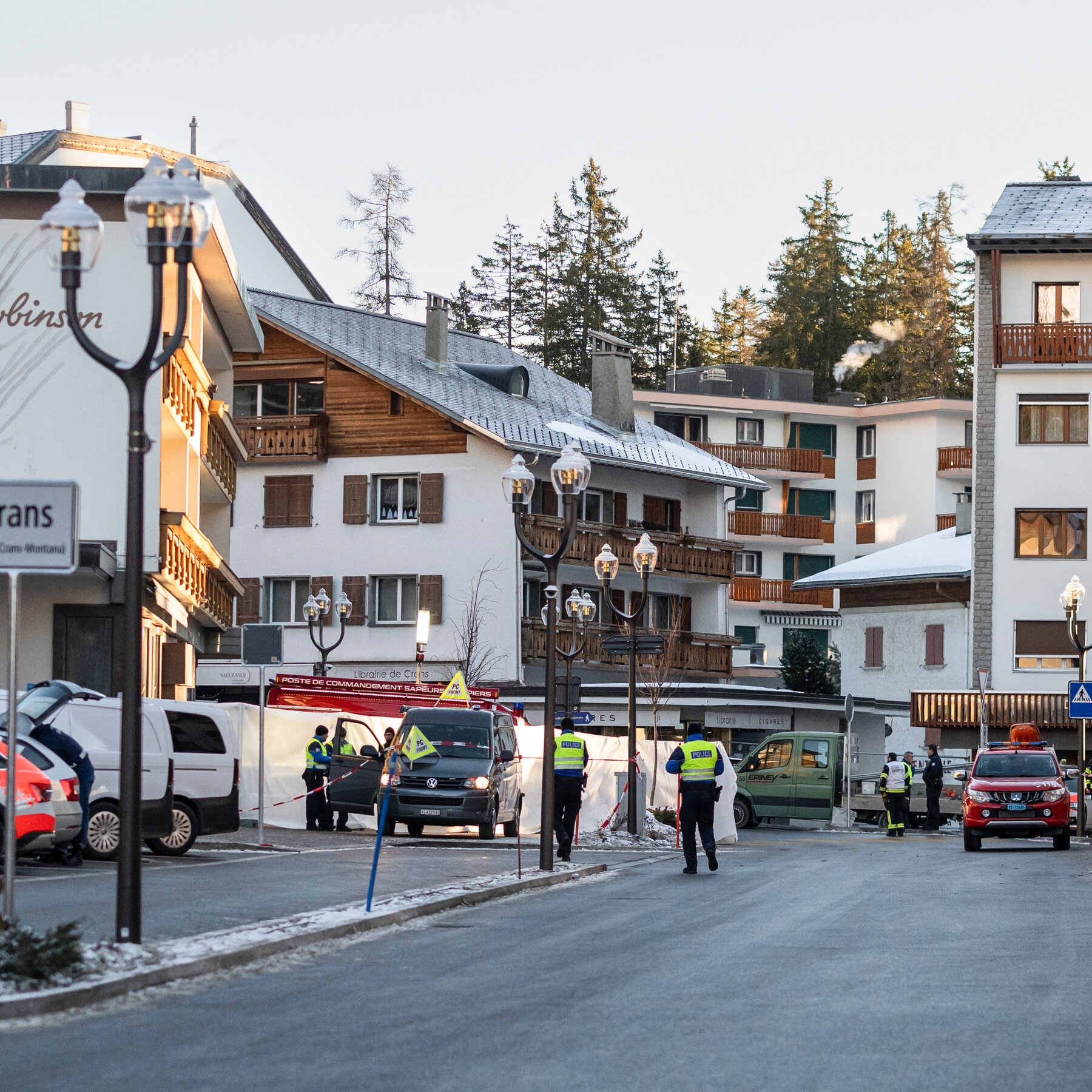

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoFire Claims Lives at New Year’s Party in Swiss Ski Resort
-

 Technology5 days ago
Technology5 days agoMajor Space Missions Set to Transform Exploration in 2026
-

 Education9 hours ago
Education9 hours agoAspen Science Center’s New Director Champions STEM Education
-

 Top Stories9 hours ago
Top Stories9 hours agoBetfred Halts ARC Racing Broadcasts Amid Rising Media Costs
-
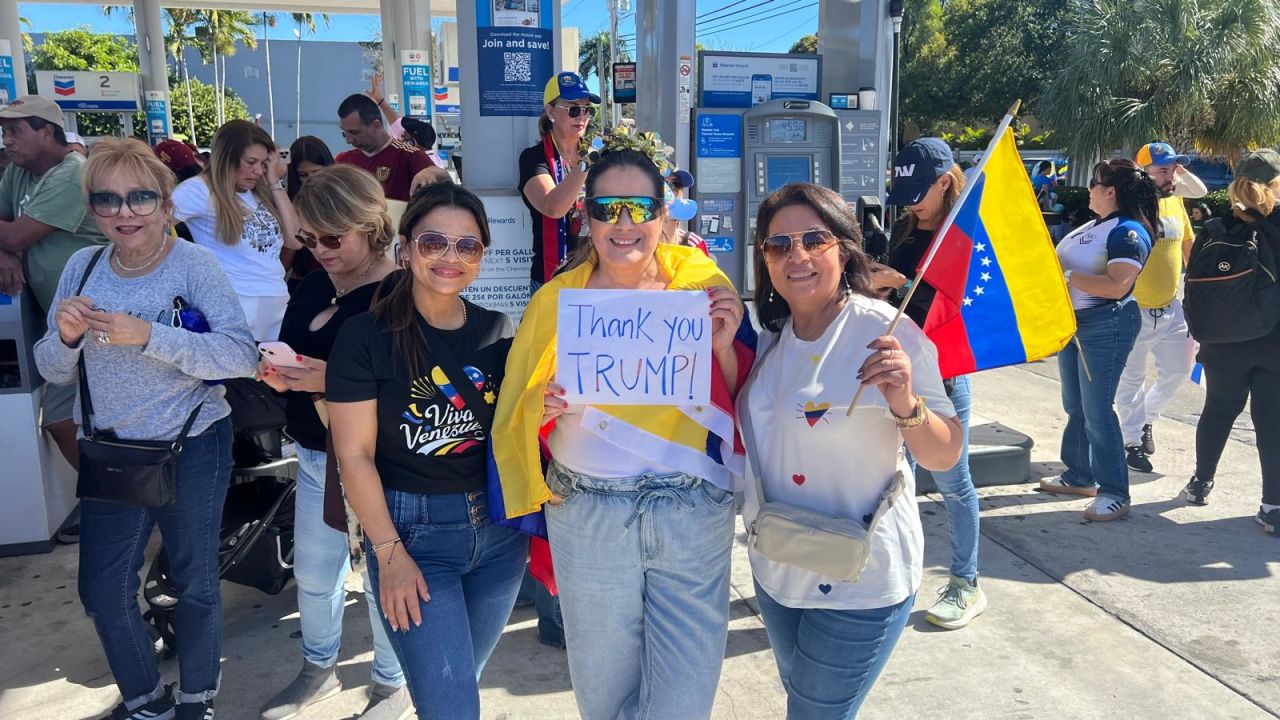

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoCrowds Erupt in Doral as Venezuelans Celebrate Maduro’s Capture





