Trump’s National Security Strategy Advocates Global Realism
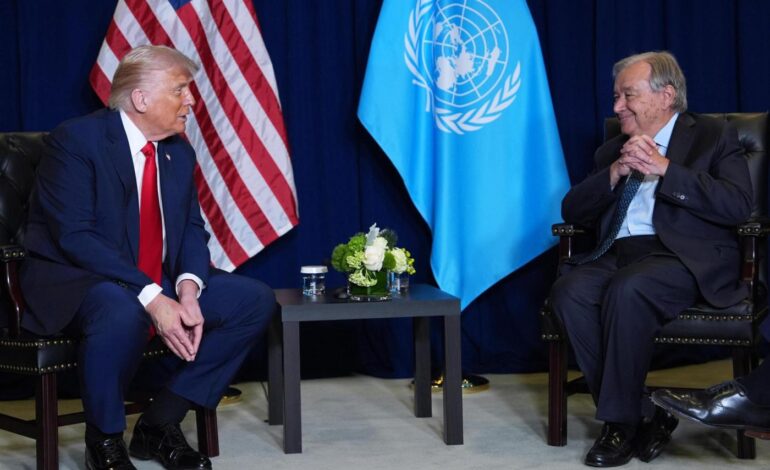

President Donald Trump unveiled his new National Security Strategy (NSS) on December 4, 2023, marking a significant shift in the United States’ military and foreign policy approach. The document emphasizes a move towards global realism, indicating that the era of U.S. dominance in global affairs is over. Instead, the strategy highlights a multipolar world where the U.S., China, and Russia are the leading powers.
In contrast to the previous NSS released by President Joe Biden in October 2022, which praised America’s alliances, Trump’s document is more assertive. He states, “In everything we do, we are putting America first,” and asserts that “the days of the United States propping up the entire world order like Atlas are over.” This reflects a broader theme of accountability, suggesting that allied nations should take more responsibility for their own defense.
The NSS critiques the past U.S. approach, which Trump claims has undermined the nation’s core values and resources. He references the estimated $8 trillion spent on post-9/11 military engagements, arguing that these funds could have been better allocated towards domestic infrastructure and competition with China.
Strategic Shift Towards Asia
The strategy notably pivots focus from Europe towards the Indo-Pacific region, where Trump asserts that nearly half of the world’s economy now resides. The NSS stresses the importance of competing effectively in this area, citing Trump’s trade agreements from his October 2025 trip to the region. Despite this, the document omits how tensions with China escalated after Trump threatened substantial tariffs, which resulted in Beijing restricting exports of rare-earth minerals crucial to U.S. industries.
Turning to the situation in Europe, Trump emphasizes the need to stabilize economies affected by the ongoing Ukraine War, describing this as a crucial American interest. He warns that Europe is facing “the stark prospect of civilizational erasure,” a statement that has stirred discontent among European leaders. The NSS calls for an end to the conflict to restore strategic stability with Russia, although it fails to address the New START Treaty, which is set to expire on February 5, 2026, and currently limits nuclear arsenals.
Challenges in the Middle East and Latin America
In the Middle East, Trump highlights successes such as the June 2025 Operation Midnight Hammer, which he claims significantly weakened Iran’s nuclear ambitions. He also points to recent achievements like the Gaza ceasefire, which he suggests could lead to lasting peace. Nonetheless, the NSS maintains a cautious tone regarding the long-term stability of the region.
The strategy’s more aggressive stance towards Latin America raises concerns. Trump invokes a modern interpretation of the Monroe Doctrine, insisting on U.S. preeminence in the Western Hemisphere. He argues that U.S. security and prosperity hinge on curbing adversarial influences, particularly from nations like Venezuela and Brazil. The NSS’s call to prohibit foreign military installations and strategic investments, especially from China, raises questions about how such measures would be enforced.
In summary, Trump’s National Security Strategy reflects a pivotal change in U.S. foreign policy, advocating for a more realistic assessment of global dynamics. While it seeks to reposition the U.S. as a more self-reliant power, the implications of this shift are yet to be fully understood. The strategy points toward a future of increased competition and potential instability in international relations.