Health
Menopausal Insomnia Affects 80% of Women; Experts Offer Solutions
A significant number of women experience insomnia during menopause, with recent studies indicating that approximately 81% of menopausal women struggle with sleep disturbances. Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in oestrogen and progesterone, contribute to these sleep issues. Symptoms like hot flushes, night sweats, and increased anxiety can further exacerbate the problem, leaving many women feeling exhausted and anxious. Experts in sleep and menopause emphasize that there are effective treatments and lifestyle changes to help manage these challenges.
Understanding Menopausal Insomnia
Insomnia is characterized by difficulty in falling asleep or staying asleep, and it can affect anyone. During menopause, women often face heightened instances of insomnia due to various bodily changes. According to Rosey Davidson, a sleep consultant at Just Chill Sleep Solutions, disruptions such as hot flashes, mood changes, and joint or muscle pain can significantly interfere with sleep. A study conducted by Kalms found that 90% of peri- and menopausal women reported experiencing disturbed sleep.
The hormonal changes associated with menopause play a crucial role in this phenomenon. Dr. Deepali Misra-Sharp, a general practitioner and women’s health specialist, notes that declining oestrogen levels impact the brain’s production of serotonin and melatonin, both essential for regulating sleep. As progesterone levels also decrease, women may find it increasingly difficult to relax and fall asleep, further compounded by midlife pressures such as work stress and family responsibilities.
Effective Strategies to Combat Insomnia
While insomnia during menopause can be challenging, experts suggest several strategies to help women regain restful sleep.
**1. Optimize Your Sleep Environment**
Creating a conducive sleep environment is vital. Dr. Misra-Sharp recommends using natural, breathable bedding made from cotton or wool, which can help wick away moisture and promote airflow. Additionally, selecting a cooling mattress made from latex rather than memory foam can enhance comfort during hot nights.
**2. Establish a Relaxing Nighttime Routine**
To combat anxiety before bed, a calming nighttime routine is essential. Dr. Khan advises incorporating relaxation techniques to soothe racing thoughts. One effective method is the box breathing technique, which involves inhaling for four seconds, holding for four, exhaling for four, and holding again. Other recommendations include winding down with dimmed lights, taking a warm shower, journaling, or sipping herbal tea.
**3. Prioritize Sleep Hygiene**
Setting the stage for sleep can significantly impact its quality. Dr. Khan suggests dimming lights an hour before bedtime to promote melatonin production and keeping electronic devices out of the bedroom to limit exposure to blue light. A clutter-free, dark, and quiet bedroom can also help facilitate uninterrupted sleep.
**4. Consider Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-i)**
CBT-i is recognized as the most effective non-drug treatment for persistent insomnia. Dr. Misra-Sharp explains that it addresses unhelpful thoughts and behaviours that contribute to sleep difficulties. Techniques such as stimulus control and sleep restriction help retrain the brain to sleep more efficiently.
**5. Explore Dietary Supplements**
Before resorting to supplements, experts emphasize the importance of a balanced diet rich in sleep-supporting nutrients. Foods high in magnesium, such as leafy greens and nuts, can aid relaxation. If dietary intake is insufficient, magnesium supplements may enhance sleep quality. Melatonin supplements can also help regulate sleep-wake cycles, particularly for those waking early in the morning.
Natural remedies such as valerian root and lavender oil are also worth considering. Studies suggest that valerian root has calming properties, while lavender oil may support relaxation, particularly in cases of anxiety-related sleep disturbances.
If insomnia persists and disrupts daily life or mood, it is advisable to seek medical advice. Dr. Misra-Sharp recommends discussing symptoms with a healthcare provider, as treatments such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT), CBT-i, or short-term medication can significantly improve sleep quality.
In conclusion, while menopausal insomnia affects a large portion of women, understanding the causes and implementing effective strategies can lead to more restful nights. With the right approach, women can navigate this challenging phase of life with improved sleep and overall well-being.
Health
Discover Top 5 Adult Briefs for Leak Prevention and Skin Health

Incontinence can disrupt daily life, affecting everything from socializing to sleep. The right adult brief can provide the necessary protection while ensuring skin health, thus enhancing comfort and confidence. With advancements in design and technology, modern adult briefs offer features like absorbent cores, leak-proof styles, and odor control, making it easier for individuals to navigate their daily routines without worry.
Selecting the appropriate adult brief may seem overwhelming due to the variety available. However, understanding key factors such as absorbency, fit, and skin safety can simplify the decision-making process. This article highlights five highly rated adult briefs that excel in leak prevention and skin protection.
1. Wellness Superio
Wellness Superio adult briefs are renowned for their effective skin protection and leak guard. Constructed from soft, breathable materials, these briefs minimize the risk of irritation while maintaining high absorbency levels. Their advanced moisture-lock technology ensures dryness over extended periods, making them ideal for heavy wetters or those requiring overnight use. The discreet design allows for comfortable wear under clothing, facilitating daily activities without anxiety.
Research supports that highly absorbent briefs with optimal moisture control help reduce skin overhydration, thus diminishing irritation risks. This underscores the importance of odor-control features in premium adult diapers, which are vital for maintaining long-term skin health.
2. Depend
Depend offers a comprehensive range of adult diapers tailored to various needs, including plus-size options. Their products prioritize leak-proof performance while ensuring skin remains dry. Featuring a discreet and flexible fit, Depend adult diapers allow for mobility without sacrificing comfort. The overnight diapers are specifically designed for heavy wetters, equipped with reinforced cores that effectively absorb large volumes of fluid, making them a preferred choice for overnight protection. Moreover, Depend’s integrated odor-control system enhances confidence in both social and professional settings.
3. Carewell
Carewell adult briefs are particularly suited for individuals with sensitive skin. Utilizing hypoallergenic materials and breathable panels, these briefs help prevent rashes and discomfort. Carewell’s premium adult pull-ons offer a comfortable fit, suitable for both active and less mobile users. Their sealed leakage system significantly reduces the risk of accidents, which is crucial for maintaining hygiene, particularly during prolonged use.
Recent studies indicate that innovations in fabric technology can support the skin microbiome, further reducing irritation and enhancing comfort. Additionally, Carewell provides 3XL and bariatric adult diaper options, catering to the needs of larger adults requiring more spacious and comfortable designs.
4. Parent Giving
Parent Giving combines affordability with high-performance features in their adult diapers. Designed to manage heavy leaks while protecting the skin from irritation, their products are effective even during nighttime use. Parent Giving emphasizes comfort with soft fabrics that minimize friction, making them convenient for daily routines, especially for those needing additional assistance. The brand is often chosen by individuals seeking reliable absorbency and a comfortable fit for everyday incontinence management.
5. North Shore Care
North Shore Care specializes in high-capacity adult briefs designed for individuals requiring maximum security. Their premium adult pull-ons and overnight diapers feature ultra-absorbent cores that effectively eliminate leakages. Rated among the best overnight briefs available, they are ideal for users producing larger volumes of fluid. With a focus on skin health, North Shore Care uses breathable materials that reduce the risk of damage, addressing a significant concern associated with long-term use of adult diapers.
In summary, selecting the right adult brief is crucial for ensuring skin protection, preventing leaks, and enhancing daily confidence. Options like Wellness Superio, Depend, Carewell, Parent Giving, and North Shore Care provide tailored solutions to meet diverse needs, including overnight protection and bariatric sizing. When choosing an adult diaper, prioritize fit, absorbency, and skin-friendly materials. A quality brief not only supports hygiene and comfort but also allows individuals to engage in daily activities with renewed confidence.
FAQs
Q1: How do I choose the right size for adult briefs?
Accurate measurements of your waist and hips are essential. Most brands provide sizing charts, and selecting the correct size is key to ensuring comfort and preventing leaks.
Q2: Can adult briefs prevent skin irritation?
Yes, briefs made with breathable materials, moisture-lock technology, and hypoallergenic features significantly lower the risk of rashes and discomfort.
Q3: Are overnight adult diapers different from regular briefs?
Yes, overnight diapers are specifically designed with higher absorbency and reinforced cores, making them suitable for extended wear and heavy wetters.
Health
Optimum Nutrition’s Protein Powder Discounted by Nearly 40%

Optimum Nutrition is currently offering a significant discount on its popular Gold Standard 100% Whey Double Rich Chocolate protein powder, bringing the price down to $32 from its original retail price of $50. The sale is available on Amazon and also extends to the vanilla flavor of the same product, making it a notable opportunity for fitness enthusiasts and health-conscious consumers alike.
For nearly a decade, this protein powder has garnered a loyal following among users. A product reviewer from The 100 Best Things Strategist Staffers described it as “a comprehensive protein source that has a smooth texture and taste.” The reviewer emphasized its digestibility and affordability, noting that it caters to a wide range of dietary needs.
Smooth Flavor and Versatile Use
The Double Rich Chocolate flavor stands out for its balanced taste. According to the reviewer, “The chocolate flavor isn’t overpowering, and the smooth consistency makes it easy to mix with water in a shaker bottle or blend into a fruit-based smoothie.” This versatility is crucial for those seeking convenient and palatable ways to increase their protein intake.
Aside from the chocolate variant, the vanilla flavor also presents an appealing option for consumers who prefer a different taste profile. The sale price of $32 makes this protein powder an attractive option in a market that frequently sees prices fluctuate.
Market Trends in Health and Nutrition
The discount comes at a time when many consumers are increasingly focused on health and wellness. Fast food chains like Shake Shack and Chipotle are adapting their menus to meet this demand, offering high-protein, lower-carb options. These changes reflect a broader trend towards more health-conscious eating habits among consumers.
As the market for nutritional supplements continues to evolve, products like Optimum Nutrition’s protein powder are likely to remain in high demand. The combination of taste, texture, and digestibility, along with a competitive price point, positions this protein powder as a strong contender for those looking to enhance their dietary protein intake.
With the sale set to attract both long-time users and new customers, the Optimum Nutrition protein powder stands out as a top option for anyone interested in maintaining or improving their nutritional regimen.
Health
U.S. Faces Surge of ‘Super Flu’ Hitting Children Hardest
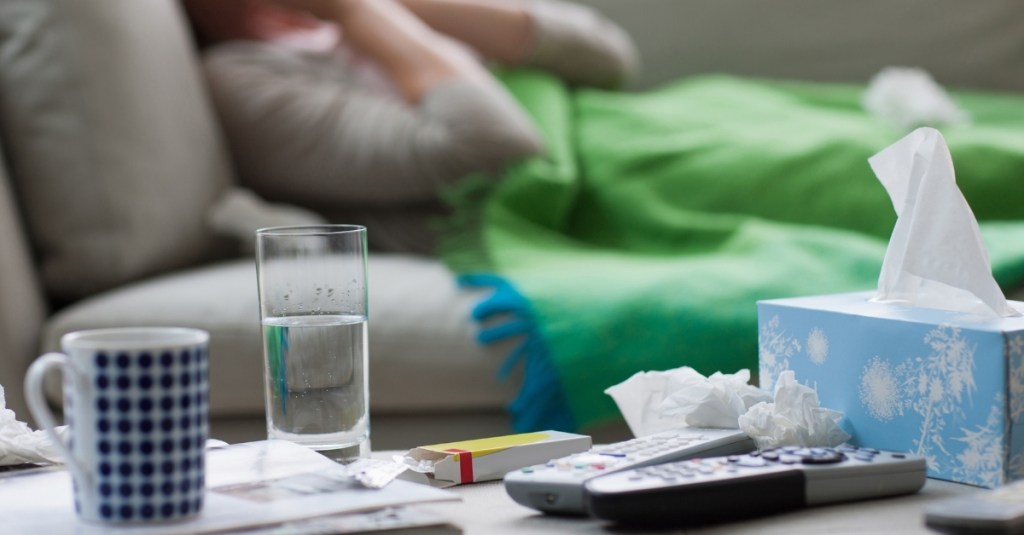

A significant surge in influenza cases, referred to as a ‘Super Flu’, is currently impacting the United States, with children suffering the most. Multiple states have reported an alarming increase in pediatric flu deaths, coinciding with a sharp rise in overall flu cases and hospitalizations across the country. Health officials attribute this winter’s unusual spike to a strain of influenza that has caught experts off guard and is now exceeding previous predictions.
According to data released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), as of December 20, 2023, flu activity was categorized as high or very high in 32 regions of the United States. Hospitalizations for flu-related illnesses have reached their third-highest level for this time of year over the past 15 seasons. Certain states, such as New York, have reported unprecedented spikes in cases, with over 71,000 positive flu cases recorded in a single week, marking the largest weekly total in the state’s history.
Children are particularly vulnerable during this outbreak. The CDC has confirmed at least eight pediatric flu deaths this season, with additional cases reported by state officials and grieving families. Both Kentucky and Ohio announced their first pediatric flu deaths within days of each other. In Minnesota, a family publicly mourned the loss of their five-year-old child due to the virus.
The Emergence of the ‘Super Flu’
Last winter, the U.S. saw an average of 280 pediatric flu deaths, and the current season appears to be on a similar trajectory. The rise of a new variant, H3N2, is contributing to this trend. While this strain is not more dangerous than typical influenza viruses, its genetic differences from anticipated strains have led to early and intense flu waves in countries such as the UK, Japan, and Australia.
The unexpected emergence of H3N2 has raised concerns about the effectiveness of the current flu vaccine. Although individuals who received their flu shots earlier in the season took the right precautionary measures, they may not have specific protection against this newly dominant strain. The vaccine administered this year does not align perfectly with H3N2, which has complicated the public health response.
As hospitals brace for continued challenges this flu season, health officials emphasize the importance of vaccination and public awareness. Families are encouraged to stay informed about flu activity in their areas and consider preventive measures to safeguard their health, especially for children who are at greater risk during this surge.
The situation remains fluid as health officials monitor the spread of the virus and assess its impact on communities nationwide. With the holiday season approaching, maintaining vigilance against influenza is crucial to mitigate further outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations.
Health
Servier Partners with Insilico to Accelerate Cancer Treatment Discovery

Servier, a French pharmaceutical company, has entered into a strategic partnership with Insilico Medicine to enhance its research and development efforts in the field of cancer treatment. This collaboration aims to leverage Insilico’s advanced artificial intelligence (AI) platform to identify and develop new therapeutic options for cancer patients.
The agreement signifies a commitment to harnessing technological advancements in drug discovery, positioning both companies at the forefront of innovative cancer research. By utilizing AI, Servier intends to streamline its processes, potentially reducing the time and costs associated with bringing new cancer therapies to market.
Innovative Approaches to Drug Development
Insilico Medicine has gained recognition for its pioneering use of AI in drug discovery, which allows for more efficient analysis of biological data and identification of potential drug candidates. This partnership will enable Servier to access Insilico’s state-of-the-art algorithms and predictive models to enhance the efficacy of its cancer treatments.
According to a statement from Servier, the collaboration is part of a broader strategy to integrate digital tools into its R&D framework. The company emphasizes the importance of innovation in oncology, particularly given the rising global incidence of cancer. With the World Health Organization (WHO) estimating that approximately 10 million people died from cancer in 2020, the need for effective treatments has never been more urgent.
Strengthening Market Position Through Collaboration
This partnership not only reflects Servier’s dedication to oncology but also highlights a growing trend in the pharmaceutical industry towards collaboration with tech firms to accelerate drug development. By combining Servier’s extensive expertise in pharmaceuticals with Insilico’s AI capabilities, the two companies aim to create a robust pipeline of new therapies.
The financial terms of the agreement have not been disclosed, but experts suggest that investments in AI-driven drug discovery can yield significant returns for pharmaceutical companies. The global market for AI in drug discovery is projected to reach $3.9 billion by 2027, according to data from ResearchAndMarkets.
As the partnership progresses, both Servier and Insilico Medicine are expected to share updates on their findings and advancements in cancer treatment research. This collaboration underscores a pivotal shift in the industry, where technology and medicine increasingly intersect to tackle some of the most pressing health challenges of our time.
In summary, the alliance between Servier and Insilico Medicine marks a significant step forward in the quest for new cancer therapies, showcasing the potential of AI to transform the landscape of drug discovery and development.
-

 Top Stories4 days ago
Top Stories4 days agoPiper Rockelle Shatters Record with $2.3M First Day on OnlyFans
-

 Top Stories3 days ago
Top Stories3 days agoUrgent Update: Denver Fire Forces Mass Evacuations, 100+ Firefighters Battling Blaze
-

 Top Stories1 day ago
Top Stories1 day agoOregon Pilot and Three Niece Die in Arizona Helicopter Crash
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoTragedy in Crans-Montana: Fire Claims Lives of Holiday Revelers
-

 Entertainment5 days ago
Entertainment5 days agoIce-T and Coco Celebrate 25 Years Together in Love and Laughter
-

 Top Stories13 hours ago
Top Stories13 hours agoMeta’s 2026 AI Policy Sparks Outrage Over Privacy Concerns
-

 Top Stories4 days ago
Top Stories4 days agoOnlyFans Creator Lily Phillips Reconnects with Faith in Rebaptism
-
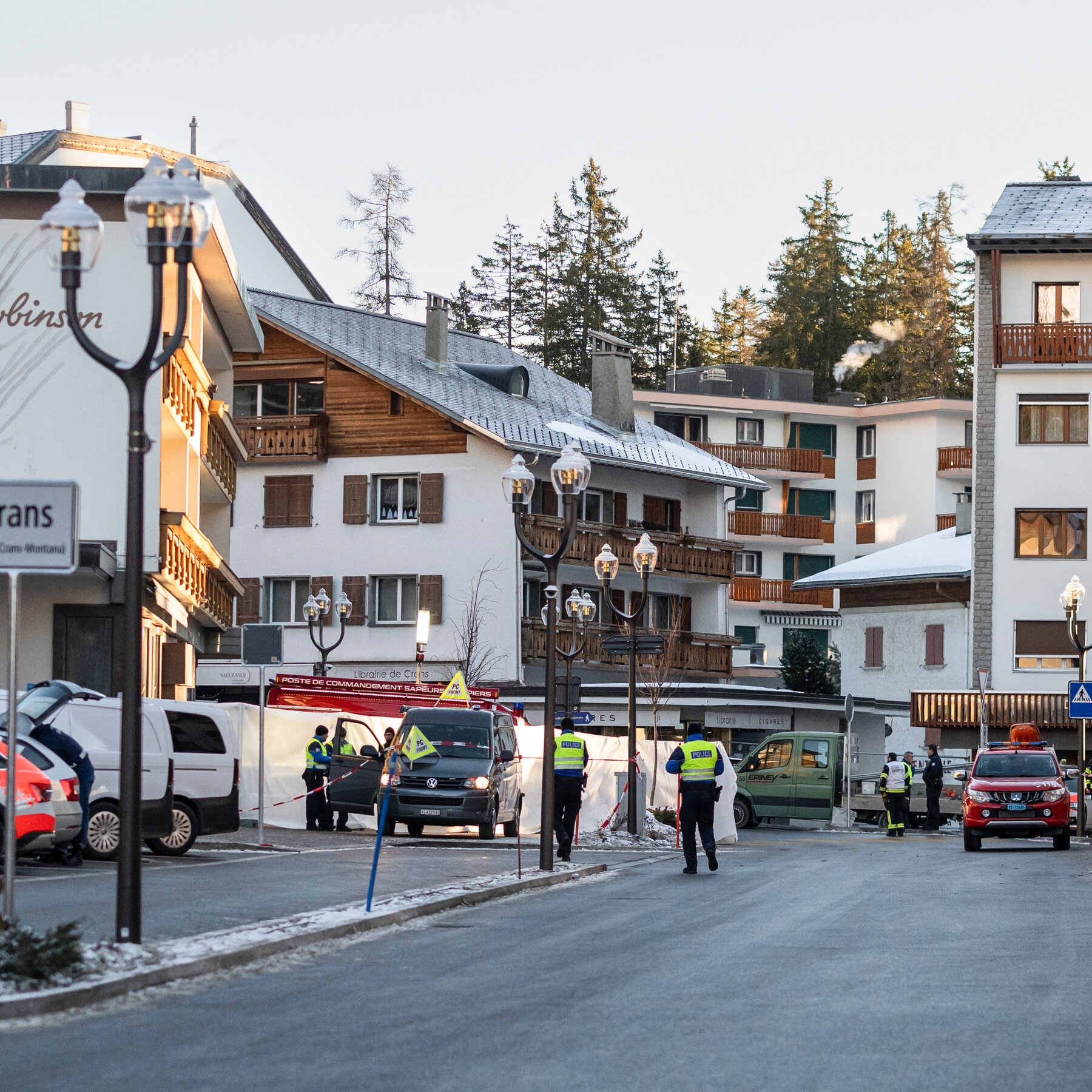

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoFire Claims Lives at New Year’s Party in Swiss Ski Resort
-

 Technology5 days ago
Technology5 days agoMajor Space Missions Set to Transform Exploration in 2026
-

 Education10 hours ago
Education10 hours agoAspen Science Center’s New Director Champions STEM Education
-

 Top Stories9 hours ago
Top Stories9 hours agoBetfred Halts ARC Racing Broadcasts Amid Rising Media Costs
-
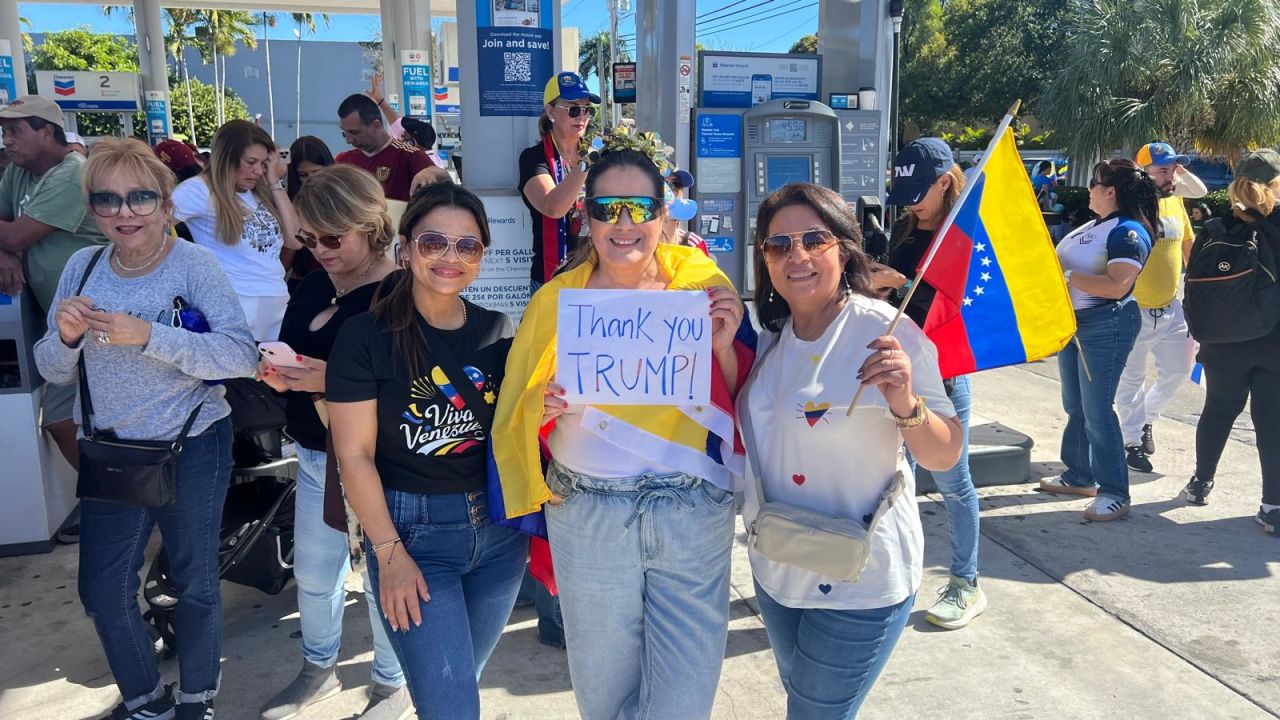

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoCrowds Erupt in Doral as Venezuelans Celebrate Maduro’s Capture





