Quantum Source Unveils Breakthrough in Photonic Quantum Computing
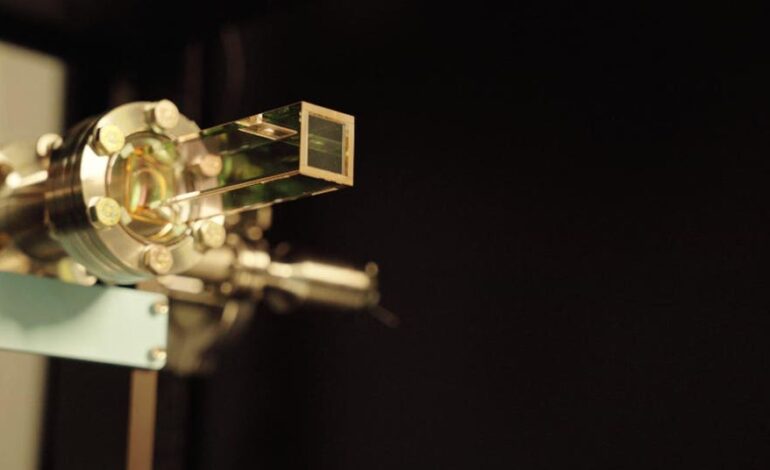
Quantum Source has announced the launch of its innovative product, Origin, marking a significant advancement in photonic quantum computing technology. This system promises to deliver fault-tolerant quantum computers that operate at room temperature, fit within standard server racks, and can scale to millions of qubits, the fundamental units of quantum information. According to co-founder and CEO Oded Melamed, Origin is scheduled for shipment to select customers in 2026, with a broader release expected in 2027.
The journey to this breakthrough began when Melamed contemplated early retirement after the acquisition of his previous company by Sony Corporation. Encouraged by industry colleagues, including Gil Semo and Dan Charash, he decided to establish Quantum Source to pursue a novel approach to photonic quantum computing, which had been conceived by Barak Dayan, a professor at the Weizmann Institute.
In April 2023, Quantum Source secured $27 million in one of the largest seed funding rounds in the quantum computing sector. It followed up with an additional $50 million in September 2024. Former Israeli Prime Minister Naftali Bennett joined the startup’s board of directors during this period. Bennett, who has a background in entrepreneurship, stated, “I got, without exaggeration, over a hundred offers from companies in Israel,” but chose to join only a select few, including Quantum Source, based on the team’s potential and the national importance of their work.
Bennett, who previously established the Israel Innovation Authority, emphasized the necessity of both private and public funding for quantum projects due to their complexities and the associated risks. He believes Quantum Source has found a “very unique angle” in its approach to quantum computing.
The quantum computing market is projected to grow from $4 billion in revenue in 2024 to as much as $72 billion by 2035, according to a recent report by McKinsey. Industries such as chemicals, life sciences, finance, and mobility are expected to drive much of this growth. In 2024, investments in quantum startups worldwide reached nearly $2 billion, reflecting a 50% increase from the previous year.
Various companies, including industry giants like Google, IBM, and Honeywell, have explored different methods of quantum computing hardware. These include trapped ions, superconducting circuits, and neutral atoms, which often require complex and costly systems. In contrast, photonic quantum computing utilizes photons, or particles of light, as qubits. This method encodes quantum information in the properties of photons, manipulating these states with optical components.
The advantages of photonic quantum computing include the capability to operate at room temperature, lower susceptibility to environmental noise, and enhanced scalability. Nevertheless, challenges remain, particularly in generating indistinguishable single photons efficiently and overcoming the probabilistic nature of photonic gates—critical components in quantum logic operations. Dayan noted, “For every photon detected, there have been roughly a million attempts.”
Quantum Source claims to have achieved a breakthrough in facilitating deterministic interactions between single atoms and photons, which is crucial for reliable quantum operations. This method allows for the generation and entanglement of photons using a minimal number of trapped atoms on each chip. Melamed remarked, “With our technology, we create this entanglement deterministically,” leading to substantially improved efficiency—about four orders of magnitude better than competing solutions.
Bennett expressed optimism for the future of Quantum Source, stating, “We’re on an adventure, facing all the dragons and fire and cliffs at the very beginning. But once we cross the chasm and get to the other side of the cliff, we can scale up limitlessly.” He sees the startup as a prime example of Israel’s innovative spirit, showcasing the potential of turning brilliant ideas into tangible solutions.






