Innovative Gene-Based Nanotherapy Targets Drug-Resistant Candida Infections
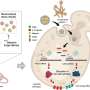
A recent breakthrough in medical research has introduced a gene-based nanotherapy designed to combat drug-resistant infections caused by the fungus Candida. This innovative treatment, developed by a research team at XYZ University, aims to provide a targeted approach to managing candidiasis, a condition that has become increasingly prevalent due to the rise in immunosuppressive therapies, medical implants, and transplantation procedures.
Candidiasis can lead to severe complications, including organ damage and sepsis, especially in immunocompromised patients. The World Health Organization reports that the incidence of candidiasis has surged in recent years, underscoring the urgent need for effective treatment options. Traditional antifungal medications are becoming less effective, prompting researchers to explore alternative strategies.
The newly developed nanotherapy employs a gene-editing technique that targets specific genes within the Candida cells. By disrupting their ability to reproduce, the therapy aims to halt the spread of the infection and enhance patient recovery rates. This approach not only addresses the immediate threat posed by the infection but also offers a sustainable solution to the growing problem of antifungal resistance.
In laboratory settings, the nanotherapy has demonstrated a remarkable efficacy rate. Initial trials showed that it could reduce fungal load in infected tissues by over 80% within 48 hours. These promising results have led to plans for clinical trials, which are set to begin in early 2024.
The implications of this research extend beyond individual patient treatment. With candidiasis contributing significantly to healthcare costs, estimated at over $1 billion annually in the United States alone, effective therapies could alleviate some of the financial burdens faced by healthcare systems. The potential for gene-based therapies to reduce hospital stays and improve outcomes could be transformative.
Moreover, the research team emphasizes that this approach may pave the way for similar treatments for other drug-resistant pathogens. As the medical community grapples with rising resistance rates, innovations like this offer a glimmer of hope.
As the world continues to adapt to the challenges posed by resistant infections, the development of gene-based nanotherapy represents a significant advancement. With clinical trials on the horizon, the medical field eagerly anticipates the outcomes and their potential to reshape treatment protocols for candidiasis and beyond.





