Exploring Self-Hosted AI: A Journey with NotebookLM
The rising interest in self-hosting Large Language Models (LLMs) has encouraged many tech enthusiasts to explore this innovative technology. One individual, seeking to understand the process of setting up a self-hosted LLM, turned to NotebookLM for guidance. This experience highlights the accessibility of complex technology through AI-assisted learning tools.
With a background in computer science and tech journalism, the writer admitted to a lack of hands-on experience in self-hosting. Despite understanding the concept, the technical jargon surrounding it was daunting. LLMs, when hosted locally, promise advantages such as enhanced performance, complete privacy, and independence from internet connectivity. However, the writer’s apprehension about navigating the technical landscape prompted a search for a more structured learning approach.
To begin the self-hosting journey, the writer initially consulted popular AI chatbots, including ChatGPT and Perplexity. Both tools provided extensive information but overwhelmed the user with dense, technical explanations. ChatGPT offered various setup methods, suggesting tools like Ollama as a local runner. Yet, the complexity of the responses made it clear that a more tailored approach was necessary.
Recognizing this, the writer opted for NotebookLM, a tool designed for personalized learning. By uploading selected sources, including guides and articles, they aimed to create a focused and manageable learning experience. One notable source was an article from XDA titled “7 Things I Wish I Knew When I Started Self-Hosting LLMs,” which provided practical insights from someone experienced in the field.
Structured Learning with NotebookLM
After setting up a NotebookLM notebook with the chosen sources, the writer initiated the learning process. Using the Chat panel, they sought a beginner-friendly explanation of self-hosting and requested step-by-step guidance based on the uploaded materials. The newly launched Learning Guide Chat mode in NotebookLM was instrumental in this process, as it adjusted explanations according to the user’s knowledge level.
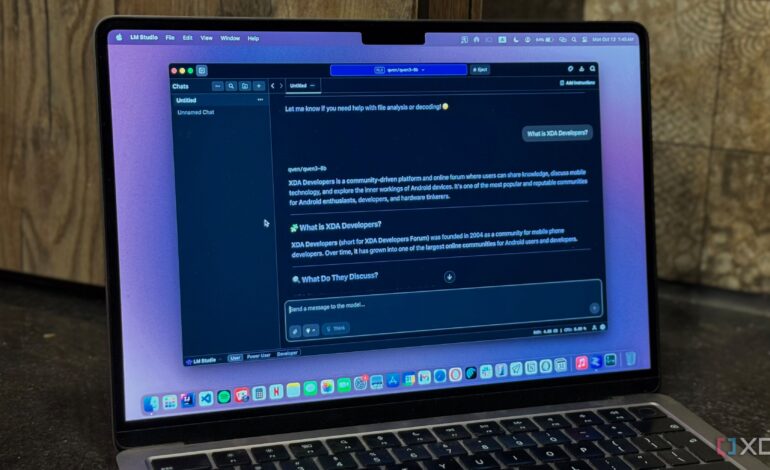
Initially, NotebookLM defined self-hosting in the context of LLMs, outlining its benefits. It then recommended starting with LM Studio, an accessible entry point for beginners. Each step was presented clearly, with the writer confirming readiness before proceeding, thus ensuring a manageable pace.
As the setup progressed, NotebookLM provided detailed instructions, addressing any questions that arose. For instance, when LM Studio began installing a model, the writer received real-time assistance in determining its suitability for their needs. In a matter of minutes, the first local AI model was operational, allowing the writer to explore its interface and test basic prompts.
The experience underscored NotebookLM’s effectiveness as a learning tool, enabling users to navigate complex topics without feeling overwhelmed. The writer, who had followed NotebookLM since its inception as a Google Labs experiment, expressed satisfaction with the results.
By successfully setting up a self-hosted LLM, the writer demonstrated that with the right resources, even those new to self-hosting can achieve their goals. This journey not only enhanced their technical understanding but also showcased the potential of AI tools in facilitating learning across various domains. The decision to leverage NotebookLM proved to be a pivotal step, transforming a once-intimidating process into an achievable task.






