NASA’s Hubble Discovers Turbulence in Planet Birthplaces
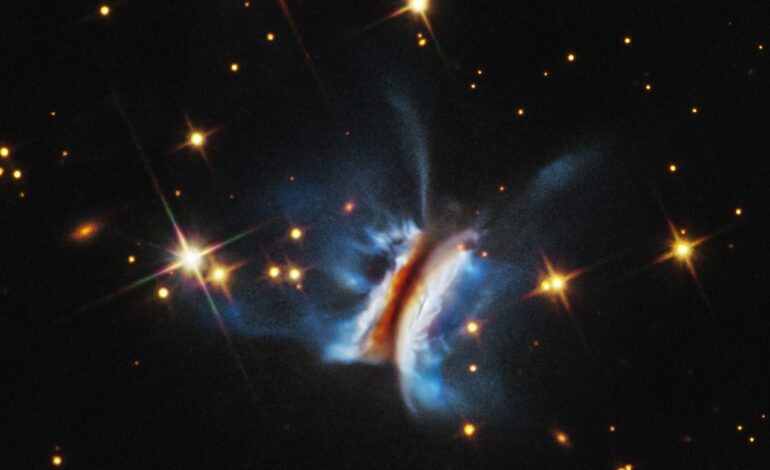

NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has detected significant turbulence in what is considered the largest observed birthplace of planets, located approximately 1,000 light-years from Earth in the Orion Nebula. This discovery sheds light on the complex processes involved in planet formation and how environmental factors can influence the development of new worlds.
The findings, published in The Astrophysical Journal, provide new insights into regions where stars and planets are born. The turbulent environment of the Orion Nebula, characterized by strong winds and intense radiation from nearby stars, plays a crucial role in shaping the conditions necessary for planet formation.
Insights from the Orion Nebula
Research led by astronomer Kristina Monsch from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics highlights the significance of turbulence in these primordial regions. The study utilized Hubble’s advanced imaging capabilities to reveal how turbulence can disrupt the formation of dust and gas aggregates, which are vital for creating planets.
Monsch emphasized that understanding these turbulent conditions is essential for unraveling the mysteries of how planets, including those potentially capable of supporting life, come into existence. The Hubble observations indicate that while turbulence can hinder planet formation, it can also create opportunities for new star formation by reshaping the environment.
The Orion Nebula is a stellar nursery, where new stars are born, and its study provides a unique laboratory for understanding not just our own solar system’s history but also the broader processes that govern the universe.
Continued Exploration and Future Implications
The implications of this research extend beyond mere academic interest. As scientists seek to understand the formation of planets in various environments, the findings could guide future missions aimed at discovering exoplanets and understanding their potential habitability.
The ongoing work of the Hubble Space Telescope continues to be instrumental in advancing our knowledge of the cosmos. With its ability to observe distant celestial bodies, Hubble remains a vital tool for astronomers.
As Joseph DePasquale, who contributed to the image processing of the Hubble data, noted, “These observations not only deepen our understanding of the turbulent environments that shape our universe, but they also inspire the next generation of astronomers to explore the final frontiers of space.”
NASA’s commitment to unveiling the mysteries of the universe through projects like Hubble underscores the importance of continued investment in space exploration. With each new discovery, we gain a clearer picture of the forces that govern our universe, opening doors to potential new worlds and the possibility of life beyond Earth.