Hubble Captures Stunning Supernova Explosion in NGC 2525
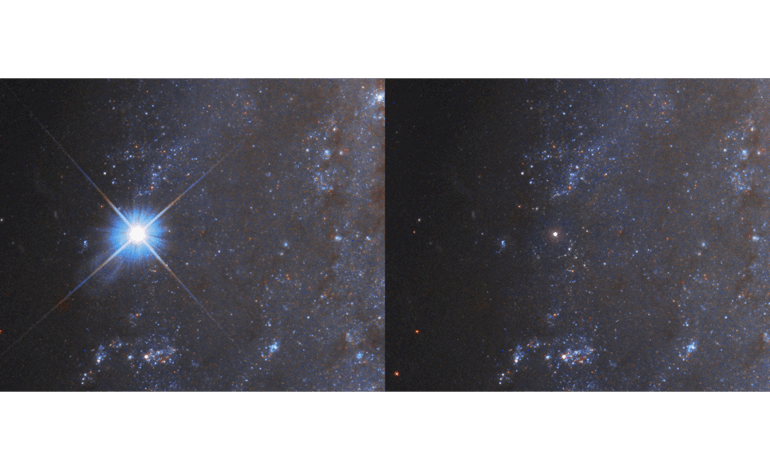

The Hubble Space Telescope has recently unveiled remarkable before-and-after images of a supernova explosion, designated as SN 2018gv. This stellar event occurred within the spiral galaxy NGC 2525, located approximately 70 million light-years from Earth. The images, taken a year apart, vividly illustrate the intense brightness of the supernova and highlight how its luminosity diminishes over time.
The supernova was first detected in early 2018 by amateur astronomer Koichi Itagaki. Following this discovery, Hubble began its observations, capturing the momentous event as it unfolded. The side-by-side comparison of the images reveals a striking contrast, showcasing the fading brilliance of SN 2018gv over the course of a year.
Understanding Type Ia Supernovae
SN 2018gv is classified as a Type Ia supernova, a particular category of stellar explosion known for its rarity. These supernovae are often referred to as “standard candles” in astronomy. They have a consistent peak brightness, allowing astronomers to measure distances in the universe with remarkable precision. By comparing their intrinsic luminosity to how bright they appear from Earth, scientists can accurately determine the distance to these cosmic phenomena.
This classification is significant not only for distance measurement but also for understanding the rate of the universe’s expansion. Type Ia supernovae play a crucial role in cosmology, providing insights into how the expansion rate has evolved over time.
NASA’s upcoming Roman Space Telescope, still under construction, aims to build upon these studies. The telescope is designed to observe such explosions in greater detail, enabling astronomers to look even further back in time than Hubble and refine the measurements of the universe’s expansion rate.
The Significance of Hubble’s Observations
The recent images captured by Hubble are not merely aesthetically stunning; they contribute to a deeper understanding of our universe. According to Martin Kornmesser and Mahdi Zamani from the European Space Agency, the ability to monitor the changes in brightness of supernovae like SN 2018gv enhances our knowledge of stellar life cycles and the dynamics of cosmic events.
Additionally, the work of Adam G. Riess and the SH0ES Team, who focus on measuring distances using Type Ia supernovae, emphasizes the importance of these observations in the broader field of cosmology. Their research helps elucidate the mysterious aspects of dark energy and the overall structure of the universe.
Hubble’s ongoing mission continues to reveal the wonders of the cosmos, and SN 2018gv serves as a striking example of how astronomical phenomena offer both visual awe and scientific insight. For those interested in learning more about the Hubble Space Telescope and its pivotal role in studying the expanding universe, further information is available on NASA’s official website.