Angola’s Start-Ups Ignite Digital Transformation Across Economy
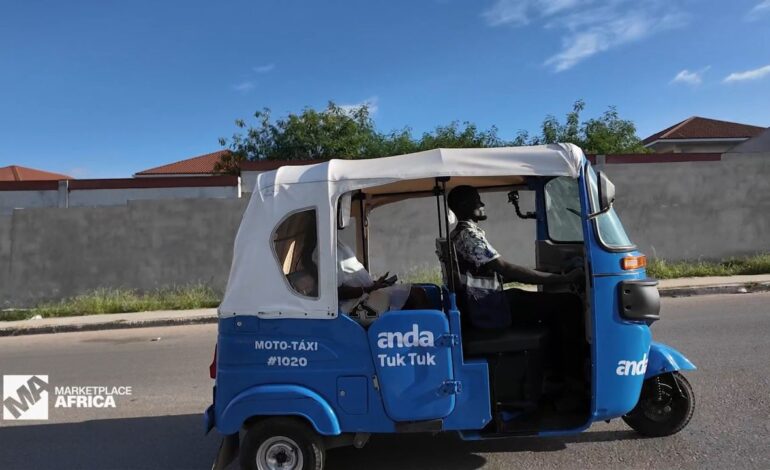

Angola is experiencing a significant shift in its economic landscape as a vibrant start-up ecosystem emerges, driving a digital revolution throughout the country. This transformation is marked by innovations in various sectors, particularly in ridesharing and food delivery services, aimed at meeting the needs of a growing middle class.
The digital economy in Angola reflects a broader trend of modernization as entrepreneurs introduce new technologies and services. With a population exceeding 32 million, the demand for efficient transportation and delivery options is on the rise. Start-ups are not only catering to this demand but also creating jobs and fostering economic growth.
Ridesharing Takes Off
One of the most notable developments is the rapid expansion of rideshare platforms in urban areas. Companies such as Yango and Bolt have established a foothold in Angola’s capital, Luanda. These platforms offer affordable transportation alternatives while providing a means for drivers to earn an income. The convenience of ridesharing has proven to be especially appealing to the country’s burgeoning middle class, who seek reliable and cost-effective travel solutions.
As of September 2023, Yango reported a user base growth of over 50% within a year, highlighting the increasing reliance on digital services. The positive reception has encouraged further investment in technology, suggesting a promising future for the sector.
Food Delivery Revolution
In parallel, the food delivery sector is experiencing a similar surge. Start-ups like Jumia Food and Glovo have capitalized on the changing consumer habits, providing a platform for restaurants to reach a wider audience. The convenience of ordering meals online has become a staple for many, especially among younger consumers who prioritize efficiency and variety.
Data shows that the food delivery market in Angola is expected to grow by 30% annually, driven by increased internet penetration and mobile phone usage. As of August 2023, Jumia Food reported a significant increase in both restaurant partnerships and customer orders, indicating a robust response to the service.
These innovations not only enhance consumer convenience but also empower local businesses. By partnering with delivery platforms, restaurants can expand their customer base without the overhead costs associated with traditional marketing and logistics.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the promising developments, challenges remain. Infrastructure issues such as inconsistent internet connectivity and limited payment options can hinder the growth of digital services. However, continued investment in technology by both local and international stakeholders is crucial to overcoming these barriers.
The Angolan government has taken steps to support the digital economy, including initiatives aimed at improving internet access and fostering entrepreneurship. According to the Ministry of Telecommunications, Information Technologies and Social Communication, efforts are underway to create a more conducive environment for start-ups, which could further accelerate growth.
As the digital landscape evolves, the role of education and skills training becomes increasingly important. Initiatives that focus on equipping young people with the necessary skills to thrive in a digital economy are essential. The collaboration between educational institutions and tech companies can provide a robust framework to nurture talent.
In conclusion, Angola’s burgeoning start-up ecosystem is driving a digital transformation that holds promise for the economy. With innovations in rideshare and food delivery, the country is positioning itself to meet the demands of an evolving middle class. As challenges are addressed and opportunities are seized, Angola may well become a notable player in the digital economy landscape across Africa.