As global meat consumption continues to rise, concerns about its environmental impact are becoming increasingly urgent. In a recent discussion with CNN’s Jake Tapper, author Michael Grunwald highlighted the unsustainable nature of current meat production practices and suggested that small dietary changes could significantly benefit the planet.
The conversation underscored the critical role of the meat industry in contributing to climate change, deforestation, and biodiversity loss. According to the United Nations, livestock production is responsible for approximately 14.5% of all anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. This statistic places the industry on par with the entire transportation sector, emphasizing the urgent need for change.
The Environmental Impact of Meat Production
Meat production is a resource-intensive process that requires vast amounts of water, land, and energy. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has repeatedly warned that reducing meat consumption is essential to meeting the goals set by the Paris Agreement. The production of beef, in particular, is a major contributor to methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas.
Deforestation is another significant concern. Large swathes of the Amazon rainforest are cleared annually to make way for cattle grazing and soy cultivation, which is primarily used as animal feed. This not only releases carbon dioxide stored in trees but also threatens countless species that depend on these ecosystems.
Small Changes, Big Impact
During the CNN interview, Grunwald emphasized that even minor adjustments in our diets can have a substantial impact. “Reducing meat consumption by just one meal a week can make a difference,” he noted. This sentiment is echoed by numerous environmental organizations advocating for a shift towards plant-based diets.
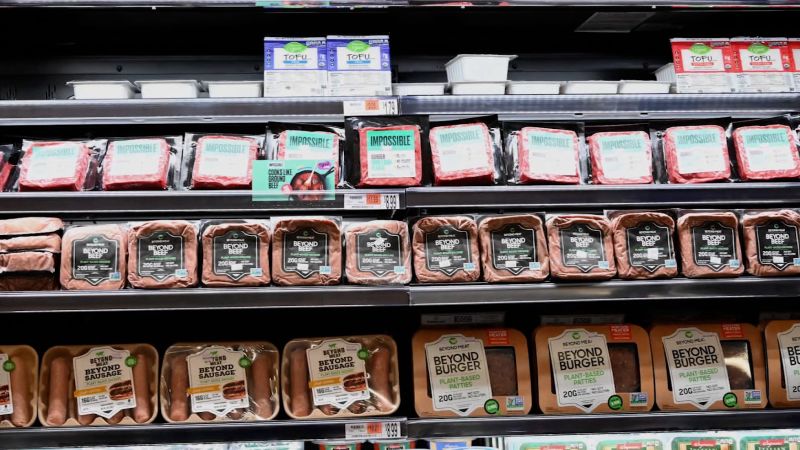
Companies like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods are leading the charge by offering plant-based alternatives that mimic the taste and texture of meat. These products are gaining popularity, with sales surging as consumers become more environmentally conscious. The World Health Organization also supports these changes, citing health benefits associated with reduced meat intake.
Historical Parallels and Future Prospects
The push for dietary change is reminiscent of past public health campaigns, such as those against smoking. Just as societal attitudes shifted over time, experts believe a similar transformation is possible regarding meat consumption. Public awareness and education are crucial in driving this change.
Looking ahead, governments and policymakers are being urged to incentivize sustainable agricultural practices and support research into alternative proteins. Initiatives like carbon taxes on meat products and subsidies for plant-based foods are potential strategies to encourage more sustainable consumption patterns.
“If we want to protect our planet for future generations, we need to rethink our relationship with food,” Grunwald stated emphatically during the interview.
Implications and Next Steps
The implications of continued high meat consumption are dire, with potential consequences including more frequent extreme weather events and further loss of biodiversity. However, the growing awareness and availability of alternatives offer hope for a more sustainable future.
As consumers, the choices we make at the grocery store and in restaurants can collectively drive significant change. By prioritizing plant-based options and supporting sustainable practices, individuals can contribute to a healthier planet.
The conversation around meat consumption and its environmental impact is gaining momentum, and as Grunwald and other experts suggest, the time for action is now. With concerted efforts from individuals, businesses, and governments, a more sustainable future is within reach.