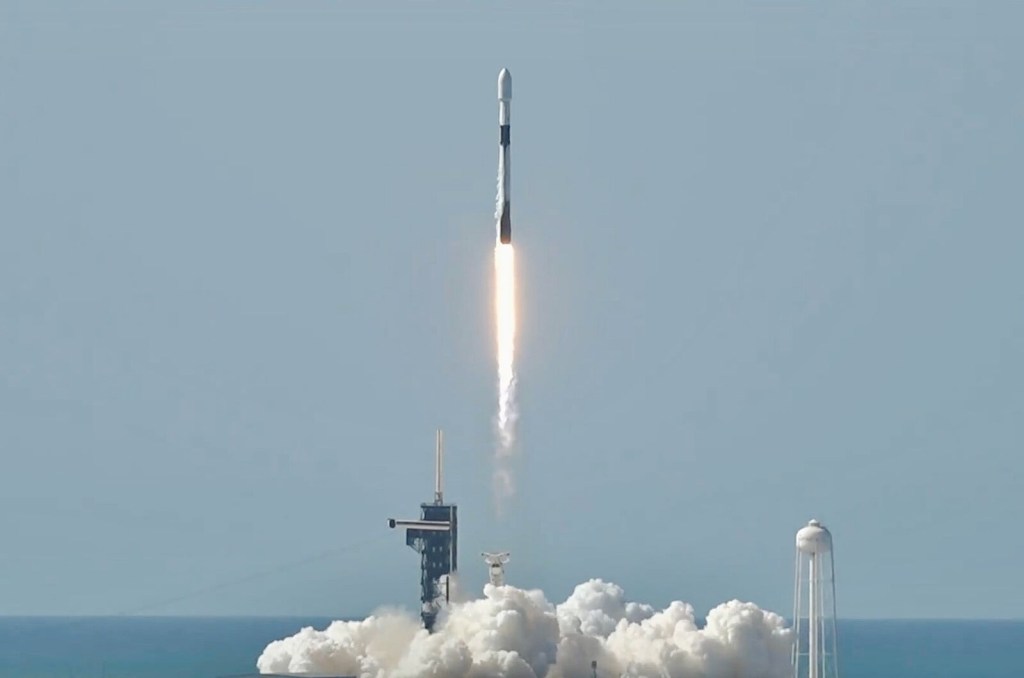
WASHINGTON — In a significant advancement for both meteorological science and environmental monitoring, a Falcon 9 rocket successfully launched a European satellite on July 1. The satellite, designed with a dual mission, aims to collect critical weather data and monitor atmospheric pollution, marking a notable collaboration between space technology and environmental science.
The launch took place from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, where the Falcon 9 rocket lifted off at precisely 3:15 PM local time. This mission underscores the growing importance of satellite technology in addressing global climate challenges and enhancing our understanding of atmospheric conditions.
Dual Mission: Weather Data and Pollution Monitoring
The satellite, part of the European Space Agency’s (ESA) ongoing efforts to improve climate science, is equipped with advanced sensors capable of providing real-time data on weather patterns and air quality. This dual-purpose mission is expected to significantly enhance the accuracy of weather forecasts and provide crucial insights into pollution levels across Europe and beyond.
According to ESA officials, the satellite will orbit the Earth at an altitude of approximately 800 kilometers, allowing it to cover vast geographical areas. Its onboard instruments are designed to measure a variety of atmospheric parameters, including temperature, humidity, and concentrations of pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide.
Historical Context and Technological Advancement
The launch of this satellite is part of a broader trend in the use of space technology to address environmental issues. Historically, satellites have been pivotal in tracking weather systems and natural disasters. However, the integration of pollution monitoring capabilities represents a significant technological advancement.
Dr. Laura Simmons, a climate scientist at the University of Cambridge, emphasized the importance of such missions. “Satellites like this one are crucial for understanding the dynamics of our planet’s atmosphere. They provide invaluable data that can lead to more effective environmental policies and strategies,” she said.
“Satellites like this one are crucial for understanding the dynamics of our planet’s atmosphere.” — Dr. Laura Simmons, University of Cambridge
Implications for Climate Science and Policy
The data collected by the satellite is expected to play a critical role in shaping future climate policies. By providing detailed and accurate information on atmospheric conditions, policymakers can make informed decisions aimed at reducing pollution and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Moreover, the satellite’s ability to monitor pollution levels in real-time offers a powerful tool for environmental agencies and researchers. This capability will enable quicker responses to pollution events and contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of how human activities impact the environment.
Looking Ahead: Future Launches and Collaborations
This successful launch is part of a series of planned missions aimed at enhancing global environmental monitoring capabilities. ESA, in collaboration with other international space agencies, plans to deploy additional satellites with similar capabilities in the coming years.
Meanwhile, SpaceX, the company behind the Falcon 9 rocket, continues to solidify its position as a leader in commercial space launches. The company’s ability to deliver payloads reliably and efficiently has made it a preferred partner for both governmental and private sector clients worldwide.
As the demand for environmental data grows, the collaboration between space agencies and commercial partners is likely to expand, paving the way for more innovative solutions to global challenges. The successful deployment of this satellite marks a significant step forward in these efforts, promising to enhance our understanding of the Earth’s atmosphere and contribute to a more sustainable future.