Federal Reserve Lowers Interest Rates Amid Economic Uncertainty
The Federal Reserve has announced a decrease in the target range for the federal funds rate by a quarter percentage point, moving it to between 4 and 4.25 percent. This decision reflects the Committee’s response to a moderation in economic growth and an increase in the unemployment rate, as indicated in their latest statement from the September 2023 Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting.
Economic indicators reveal that growth slowed during the first half of the year. While job gains have decelerated, the unemployment rate remains low, suggesting a mixed economic landscape. Inflation has risen and remains somewhat elevated, prompting the Committee to reaffirm its commitment to achieving maximum employment while targeting an inflation rate of 2 percent over the long term.
The FOMC highlighted the continuing uncertainty surrounding the economic outlook, noting an increase in downside risks related to employment. The decision to lower the interest rate reflects a strategic response to these evolving challenges. As part of its ongoing strategy, the Committee plans to continue reducing its holdings of Treasury securities and agency debt, as well as agency mortgage-backed securities.
In making future adjustments to the federal funds rate, the Committee will carefully evaluate incoming data, the changing economic landscape, and the balance of associated risks. The FOMC underscored its readiness to modify its policy stance if necessary to support its goals.
FOMC Members’ Votes and Economic Projections
The monetary policy action received support from key members of the FOMC, including Jerome H. Powell, Chair; John C. Williams, Vice Chair; and Michael S. Barr, among others. Notably, Stephen I. Miran opposed the measure, advocating for a more significant cut of half a percentage point at this meeting.
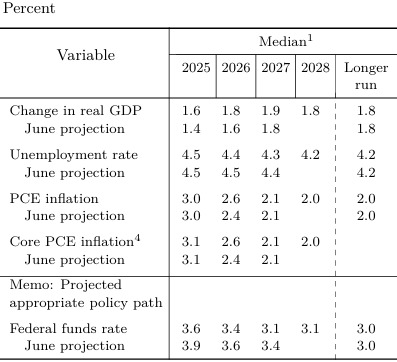
Looking ahead, projections indicate a potential for an additional 25 basis point reduction by the end of the year. The Federal Reserve anticipates the gross domestic product (GDP) growth rate to decrease from 3.9 percent to 3.6 percent this year, with expectations for a further decline to 3.4 percent by 2026. The outlook for inflation remains cautious, with the Committee not expecting inflation to return to the 2 percent target until 2028.
The FOMC’s latest assessment showcases a proactive approach to navigating an economic environment marked by uncertainty. As it continues to monitor a wide range of factors—including labor market conditions, inflation pressures, and global developments—the Federal Reserve remains committed to its dual mandate of promoting maximum employment and stable prices.