Researchers Uncover Genetic Mechanism Behind Lilac Flower Fading
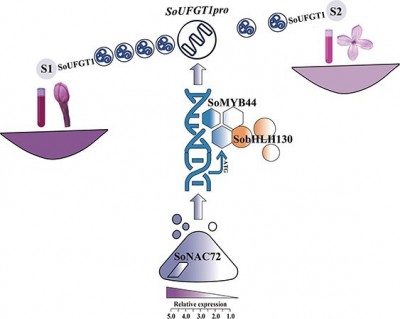
A research team has identified the molecular mechanism responsible for the fading of lilac flowers, specifically the species Syringa oblata. This discovery addresses a long-standing question in the field of ornamental plant biology and enhances the understanding of how flower coloration is regulated.
The study revealed a critical regulatory module known as SoNAC72-SoMYB44/SobHLH130, which plays a pivotal role in the biosynthesis of anthocyanins. These pigments are essential for the vibrant purple coloration that lilacs are known for. As the flowers age, their color diminishes, a phenomenon that has intrigued botanists and horticulturists alike.
Understanding the genetic basis of flower coloration is not merely an academic pursuit. The findings could have significant implications for the ornamental plant industry, particularly in enhancing flower longevity and color retention. This might lead to the development of more resilient plant varieties that maintain their aesthetic appeal longer, which is crucial for both growers and consumers.
Implications for the Ornamental Plant Industry
The research, published on October 10, 2023, provides insights that could transform the way breeders approach the cultivation of lilacs and other flowering plants. By manipulating the identified genetic module, it may be possible to create cultivars with improved color retention and overall vitality.
The ornamental plant market, valued at approximately $25 billion globally, stands to benefit from these advancements. Enhanced flower durability could lead to increased sales and consumer satisfaction, particularly as demand for vibrant, long-lasting blooms continues to rise.
Furthermore, the study emphasizes the importance of genetic research in agriculture and horticulture. As climate change and environmental challenges impact plant growth, understanding the genetic factors that influence flower quality becomes even more critical.
Future Research Directions
The research team is now focused on further exploring the interactions between various genetic components involved in flower pigmentation. Future studies could aim to identify additional genes that contribute to color dynamics and investigate their potential applications in other ornamental plants.
As the scientific community continues to unravel the complexities of plant genetics, the hope is that such discoveries will lead to innovative solutions that enhance not only the beauty of flowers but also their resilience in changing environments.
This groundbreaking research underscores the intersection of science and horticulture, illustrating how a deeper understanding of genetics can lead to practical advancements in the ornamental plant sector. The exploration of flower color dynamics is just one example of how molecular biology can impact the way we cultivate and appreciate nature.