NASA Discovers Signs of Life on Mars; Scientists Create Visible Time Crystals
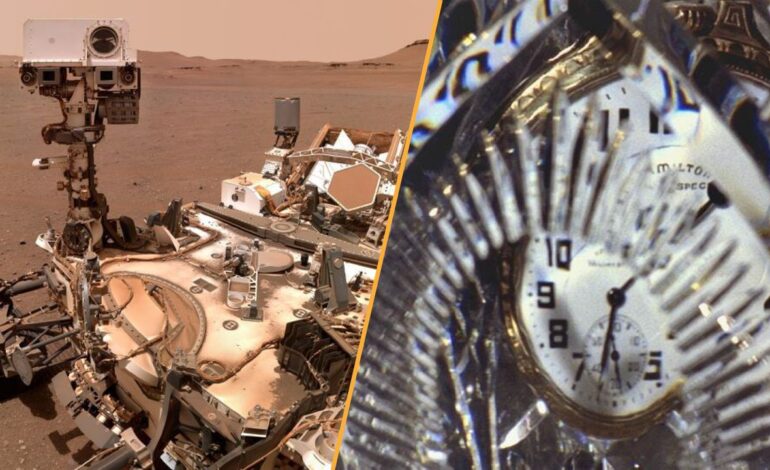

This week has brought significant advancements in scientific discovery, highlighted by NASA’s announcement regarding potential signs of life on Mars. Researchers have identified rocks on the Martian surface that contain distinct speckled patterns, which on Earth are indicative of microbial activity. Alongside the presence of organic compounds and evidence that water once flowed through these rocks, the findings have sparked excitement among scientists. Nevertheless, caution remains as alternative explanations, such as inorganic processes, could account for these markings. Confirmation of biological origins will hinge on the politically sensitive Mars Sample Return mission.
Gravitational Waves and Time Crystals
In another groundbreaking development, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) has confirmed a long-held theory by the late physicist Stephen Hawking. By detecting subtle ripples in space-time resulting from the merger of two distant black holes, LIGO has illustrated a connection between general relativity and quantum mechanics. This discovery could pave the way for unifying these fundamental theories into a “theory of everything.” However, any future investigation into black holes may require significant advancements in cellular engineering, particularly in light of recent findings regarding accelerated aging in human stem cells exposed to space conditions.
Additionally, scientists have made strides in the field of quantum physics by successfully creating visible time crystals. The new time crystals, which are formed from materials typically found in LCD screens, represent a remarkable leap from theoretical concepts first proposed in 2012 and previously realized in 2016. These structures not only demonstrate the peculiar properties of time crystals but could also have practical applications, such as anti-counterfeiting designs for high-denomination currency.
Mysterious Barrels Off Los Angeles
In environmental news, researchers have begun to unravel the mystery surrounding a graveyard of 27,000 barrels discovered submerged off the coast of Los Angeles. Initially believed to contain the banned pesticide DDT, recent studies analyzing samples from five of the barrels revealed they actually hold caustic alkaline waste capable of harming marine ecosystems. The research team is now working to determine the full extent of the toxic spill and the chemical reactions that formed the surrounding sediment haloes.
Scientists also reported on the ongoing impact of climate change, noting the near-collapse of a critical Atlantic current and the shattering of the world’s largest iceberg. These developments serve as stark reminders of the pressing need for comprehensive climate action. Meanwhile, the potential for future exploration beyond our solar system remains tantalizingly close, with discussions surrounding a hypothetical 400-year journey to Alpha Centauri gaining traction.
As scientists continue to explore these and other phenomena, the quest for knowledge remains as dynamic as ever. The discoveries made this week underscore the importance of continued investment in scientific research and environmental stewardship.